Base editor screening for gene functions¶
Summary¶
Base editor-based gene disruption tend to have less noise than cas9-based methods. Below is the design flowchart.
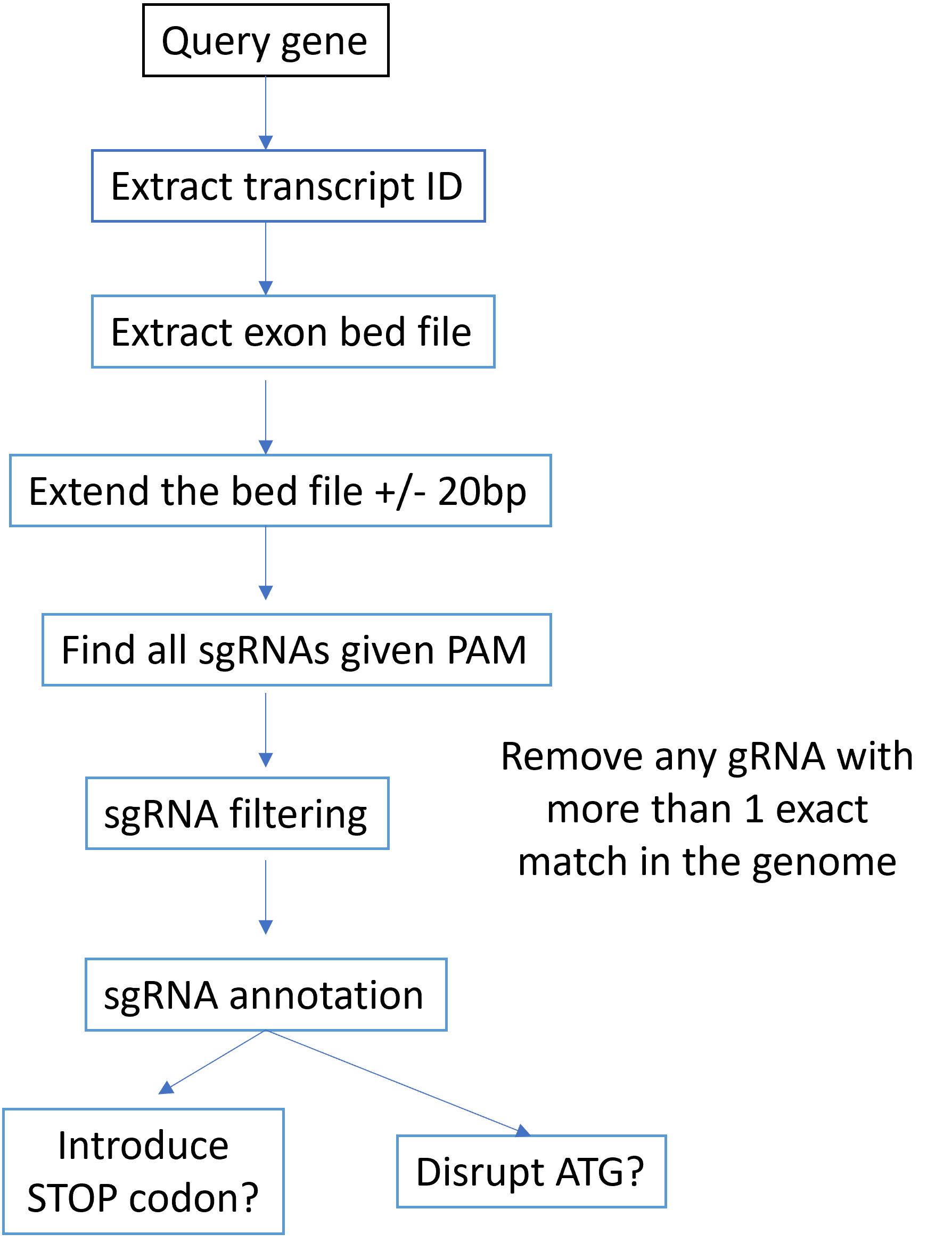
Input¶
The program needs the following inputs:
Gene Name. Type: str.
PAM. Type: str.
ATG positions. This can be a dictionary for position annotation. For example, GATA1 has two start codons, one for GATA1 full length, the other for GATA1 short. Type: dict.
iSTOP prediction results. Type: file
Output¶
Output file name is {{gene_name}}.gRNA.annot.tsv
Candidate gRNA bed6 file, with additional columns of is_iSTOP and is_ATG. iSTOP is a tool for STOP codon mutation gRNA design. is_ATG indicates if this gRNA disrupts the start codon.
Usage¶
BE_gRNA_design.py GATA1 NG "{'GATA1Full': [48791110, 48791111], 'GATA1s': [48791873, 48791874]}" ../GATA1-istop.csv
BE_gRNA_design.py RPS19 NG "{'RPS19_main': [41860775, 41860776], 'RPS19_ENST00000221975': [41869081, 41869082]}" /home/yli11/Share/John/RPS19-istop.csv
R code to run iSTOP¶
CHANGE gene name as needed.
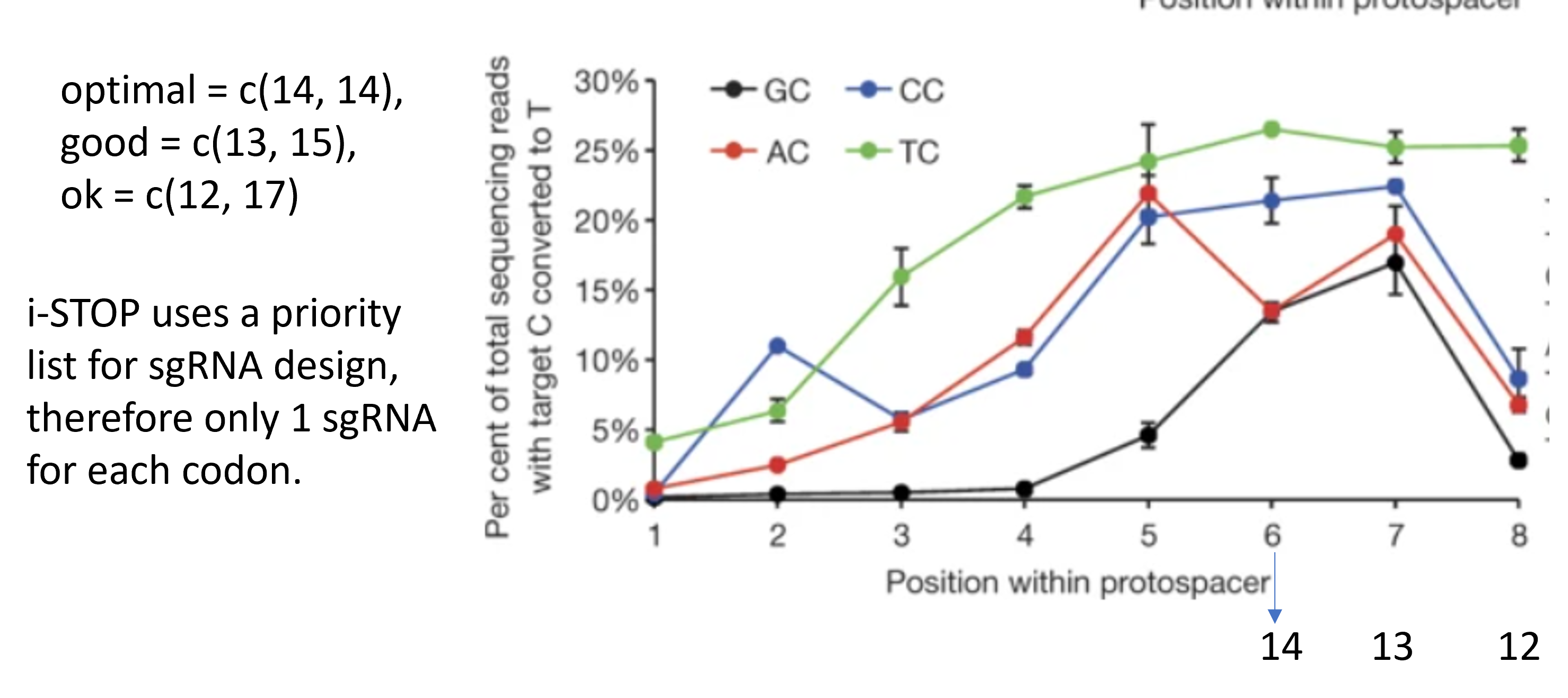
library(tidyverse)
library(iSTOP)
CDS_Human <- iSTOP::CDS_Hsapiens_UCSC_hg38()
Genome <- BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg38::Hsapiens
BE_spacing=PAM_spacing(optimal = c(14, 14), good = c(13, 15), ok = c(12, 17))
PAM_list=PAM_patterns_default(
sgNGG = PAM_pattern(".GG", 3),
sgNG = PAM_pattern(".G", 2),
sgNGA = PAM_pattern(".GA", 3),
sgNGCG = PAM_pattern(".GCG", 4),
sgNGAG = PAM_pattern(".GAG", 4),
sgNNGRRT = PAM_pattern("..G[AG][AG]T", 6),
sgNNNRRT = PAM_pattern("...[AG][AG]T", 6),
)
GATA1 <-
CDS_Human %>%
filter(gene == 'GATA1') %>%
locate_codons(Genome) %>%
locate_PAM(Genome,PAM=PAM_list,spacing=BE_spacing)
readr::write_csv(GATA1,"GATA1-istop.csv")