NGS pipelines¶
- Standard GATK variant calling for both human and non-human species
- MNase-seq analysis pipeline (not a standard version)
- MicroC data analysis pipeline
- MinION Nanopore for sequence assembly and read mapping
- Create normalized RNA-seq bigwiggle files
- RNA velocity analysis
- Analysis of single cell Strand-seq data
- Analysis of Sci-L3-seq data
- Targeted methyl-seq amplicon analysis
- RNA-seq alternative splicing pipeline
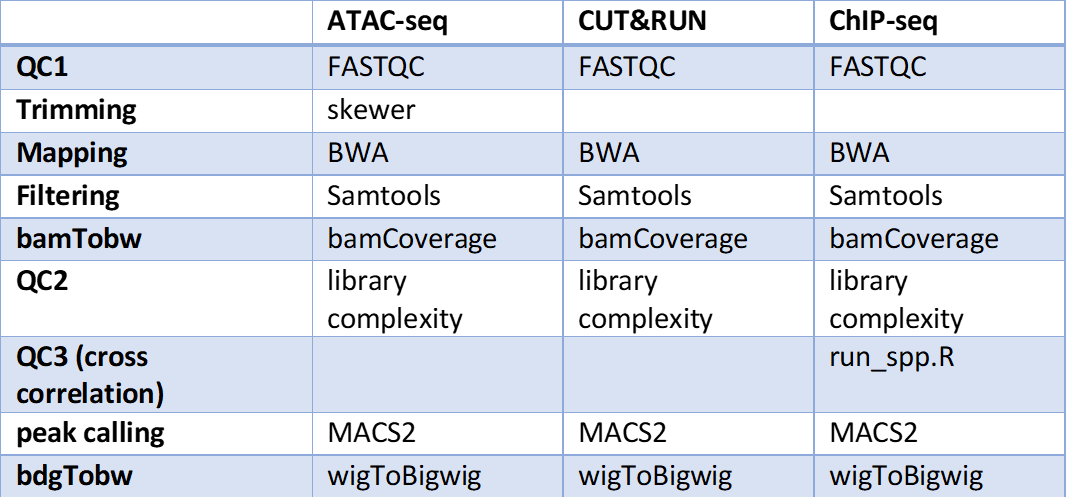
- ATAC-seq
- Footprint analysis for ATAC-seq data
- STARR-seq analysis pipeline
- Running just BWA mem mapping
- CaptureC data analysis pipeline
- CHANGE-seq analysis pipeline
- Paired-end ChIP-seq
- Single-end ChIP-seq
- CITE-seq (scRNA-seq with antibodies) analysis
- Genome-wide CRISPR Screening
- CUT & RUN pipeline
- CUT & RUN calibration pipeline
- Cut & RUN footprinting
- nfcore pipelines for CUT-RUN, CUT-Tag, and TIPseq
- Differential exon analysis
- RNA-seq: differential gene expression analysis
- eCLIP-seq data analysis pipeline
- gCrisprTools: Genome-wide CRISPR Screening
- RNA-seq: Identification of gene fusion events
- Detecting allele-specific effects on ChIP-seq or ATAC-seq
- Analysis of Hi-C or HiChIP data
- MNase-based HiCHIP data analysis
- Analysis of Hi-C and capture-C data using HiC-Pro
- Paired-end histone ChIP-seq or CUT&RUN
- Call IDR peaks given bam files from two replicates
- PacBio iso-seq data analysis
- DNA methylation (Bisulfite-Sequencing) analysis pipeline using nf-core
- Call motif footprint from bigwiggle files
- Inspection of multi-mapped reads
- Sequencing-depth and fragment-length normalized bigwiggle track
- Sequencing-depth and fragment-length normalized bigwiggle track
- Total reads in peaks normalized bigwiggle track
- Variant calling on PacBio HIFI reads
- Summerize R1 R2 read mapping direction and distance
- RNA-seq: Transcript-level quantification
- Variant identification on RNA-seq data
- scJupyter for single cell integration, annotaiton, modeling and reporting
- SHARE-seq data analysis
- Single-cell RNA-seq analysis
- Single-cell RNA-seq analysis
- Single-cell multiomc analysis
- SLAM-seq for time-resolved RNA sequencing
- NCBI download GEO/SRA data
- STARR-seq analysis pipeline
- Target-Seq analysis
- HemTools Tutorial 4-18-2019
Typical Usage¶
Go to your data directory and type the following.
Step 0: Load python version 2.7.13.
$ module load python/2.7.13
Step 1: Prepare input files, generate fastq.tsv and peakcall.tsv.
Note
peakcall.tsv is not generated for atac_seq subcmd, since no control is needed for ATAC-seq. –guess_input option is not available for crispr_seq subcmd.
$ HemTools [subcmd] --guess_input
Input fastq files preparation complete! ALL GOOD!
Please check if you like the computer-generated labels in : fastq.tsv
Input peakcall file preparation complete! File name: peakcall.tsv
Note
If you are preparing fastq.tsv and peakcall.tsv yourself, please make sure no space anywhere in the file. Note that the seperator is tab. Spaces in file name will cause errors.
Step 2: Check the computer-generated input list (manually), make sure they are correct.
$ less fastq.tsv
$ less peakcall.tsv
Note
a random string will be added to the generated files (e.g., fastq.94c049cbff1f.tsv) if they exist before running step 1.
Step 3: Submit your job.
$ HemTools [subcmd] -f fastq.tsv -d peakcall.tsv
You can always see all available sub-commands by:
$ HemTools -h
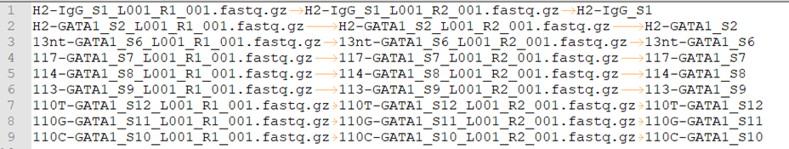
Sample input format¶
fastq.tsv
This is a tab-seperated-value format file. The 3 columns are: Read 1, Read 2, sample ID.
peakcall.tsv
This is also a tab-seperated-value format file. The 3 columns are: treatment sample ID, control/input sample ID, peakcall ID.

Report bug¶
Once the job is finished, you will be notified by email with some attachments. If no attachment can be found, it might be caused by an error. In such case, please go to the result directory (where the log_files folder is located) and type:
$ HemTools report_bug
Output¶
A QC report will be sent to you by email when the job is done.
For .bw .bam and peak files, we provide the following types:
all (all reads are kept)
rmdup (PCR duplicates are removed, note that these are just reads with the same 5’ end position)
rmdup.uq (i.e., disticnt reads, PCR duplicates and multi-mapped reads are removed)
markdup.uq (only multi-mapped reads are removed)
Multi-mapped reads are removed using samtools view -q 1; this typically removes almost 99% multi-mapped reads, but some will be still there.
For common usage, use rmdup.uq. When you focus on dulicated regions, e.g., HBG1/HBG2, you might want to use rmdup or all.
For RNA-seq, use markdup.uq.
For short length single-end chip-seq, use markdup.uq.
Comments¶
code @ github.