Analysis of Hi-C and capture-C data using HiC-Pro¶
usage: hicpro_batch.py [-h] [-j JID] [--addon_parameters ADDON_PARAMETERS]
[--queue QUEUE] (-f FASTQ_TSV | --guess_input)
[-g GENOME] [-e DIGESTED_ENZYME]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-j JID, --jid JID enter a job ID, which is used to make a new directory.
Every output will be moved into this folder. (default:
hicpro_batch_yli11_2021-04-30)
--addon_parameters ADDON_PARAMETERS
addon parameters passed to hicpro split (default:
None)
--queue QUEUE
-f FASTQ_TSV, --fastq_tsv FASTQ_TSV
tab delimited 3 columns (tsv file): Read 1 fastq, Read
2 fastq, sample ID (default: None)
--guess_input Let the program generate the input files for you.
(default: False)
Genome Info:
-g GENOME, --genome GENOME
genome version: hg19, hg38, mm9, mm10. By default,
specifying a genome version will automatically update
index file, black list, chrom size and
effectiveGenomeSize, unless a user explicitly sets
those options. (default: hg19)
-e DIGESTED_ENZYME, --digested_enzyme DIGESTED_ENZYME
digested_fragments hg19_MboI (default: MboI)
Summary¶
This program provides Hi-C or Capture-C data analysis paired-end samples, split the fastq files and run HiC-Pro.
Total input reads is splited to 100M reads per file. So a 1.5B reads will generate 15 splited files, each will be submited to HPC. Mapping takes about 20 hours for 100M PE reads. Combining the reads and remove duplicates are much faster, about 3 hours. ice takes about 3 hours. hicpro2juicer takes about 50 hours. So together, you should have the results within a week.
This program is updated for processing multiple samples. See old hicpro_split.py usage in the very bottom of this page.
Currently, hicpro_batch.py only support standard HiC analysis. hicpro_split.py provides options to keep duplicated and multi-mapped reads and capture-C data analysis.
Note: Homer has a problem converting working with --keep_dup option. Usually, we don’t keep duplicates, we only did it for 20copy project.
HiC-Pro configuration file can be found at: “https://github.com/YichaoOU/HemTools/blob/master/share/NGS_pipeline/hicpro.config”.
Actual code for this pipeline can be found at: “https://github.com/YichaoOU/HemTools/blob/master/share/lsf/hicpro_split.lsf”
Usage¶
Go to your fastq files folder and do the following:
hpcf_interactive
module load python/2.7.13
hicpro_batch.py --guess_input
hicpro_batch.py -f fastq.tsv -g hg19 -e MboI
-e Mbol is the digested enzyme. Supported enzymes are MboI or DpnII (these two all cut ^GATC, so please just use MboI), NlaII, and HindIII.
To run captureC data in batch mode, put the fastq files that use the same bait in the same dir, and type:
hpcf_interactive
module load python/2.7.13
hicpro_batch.py --guess_input
hicpro_batch.py -f fastq.tsv -g hg19 --addon_parameters " -t target.bed -e NlaIII"
Output¶
Same output as described in hic_hichiper pipeline
QC report¶
Multi-QC HTML report¶
You should be able to find multiqc_report.html in the hicpro_results folder.
HicPro QC figures¶
They are in hicpro_results/hic_results/pic/
There is a known bug that the labels in plotMapping.pdf are wrong: https://github.com/nservant/HiC-Pro/issues/290.
QC considerations¶
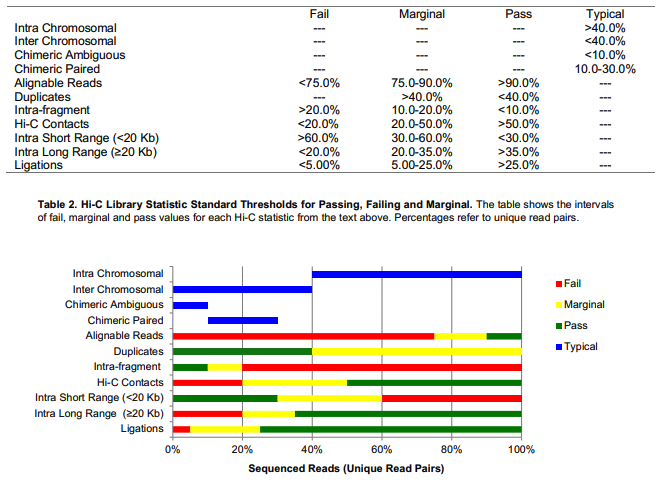
Browser view is here: https://ppr.stjude.org/?study=yli11/phil/hic.json, we can see the data range (the HiC matrix and TAD score) for Hudep2 WT and Single Gamma is different. I think this is primarily due to difference in data quality. Looks like Hudep2_WT is still in low quality. According to ENCODE standards ( ), it did have >90% alignment rate, <40% duplication rate, >50% valid interactions, but long-range intra-chromosome interactions (>20kb) is only 17%, falls below the “marginal” flag range, which is 20% to 35%. (SingleGamma sample is 28%).
Hudep2 WT and Single Gamma are also in different sequencing depth. I tried down-sample them to 100M valid pairs, but the HiC matrix and TAD scores are still in quite different range.
ref: https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-019-1658-7
alignment
Overall > 90% aligned PE reads
< 100M mapped pairs is considered to be shallow
Duplicated pairs
< 40% Analysis of 13 cell types, most of them <30%: https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-019-1658-7
Capture C may have higher % duplication due to high number of PCR cycles (NG capture, 20-24 cycles, compared to 11 cycles typically for PCHi-C) and higher sequencing depth. Just remove them: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6102006/
For promoter capture HiC, with/w.o duplicates, the tracks look very similar, see s figures in: https://www.nature.com/articles/ng.2871
Valid interactions
> 50%
Number of intra-chromosomal interactions (In multiQC html,
Contact Statistics, unique cis interactions )
This metric will affect A/B compartment and TAD calling
short-range (<20kb) cis unique interactions > 60% failed, 30-60 marginal, <30% is good
long-range (>20kb) cis unique interactions < 20% is failed, 20-40% is marginal, >40% is good
1M - 5M is considered to be the minimal usable data.
< 20M seems to have lower reproducible rate.
> 30M is normal
> 400M is deeply sequenced data.
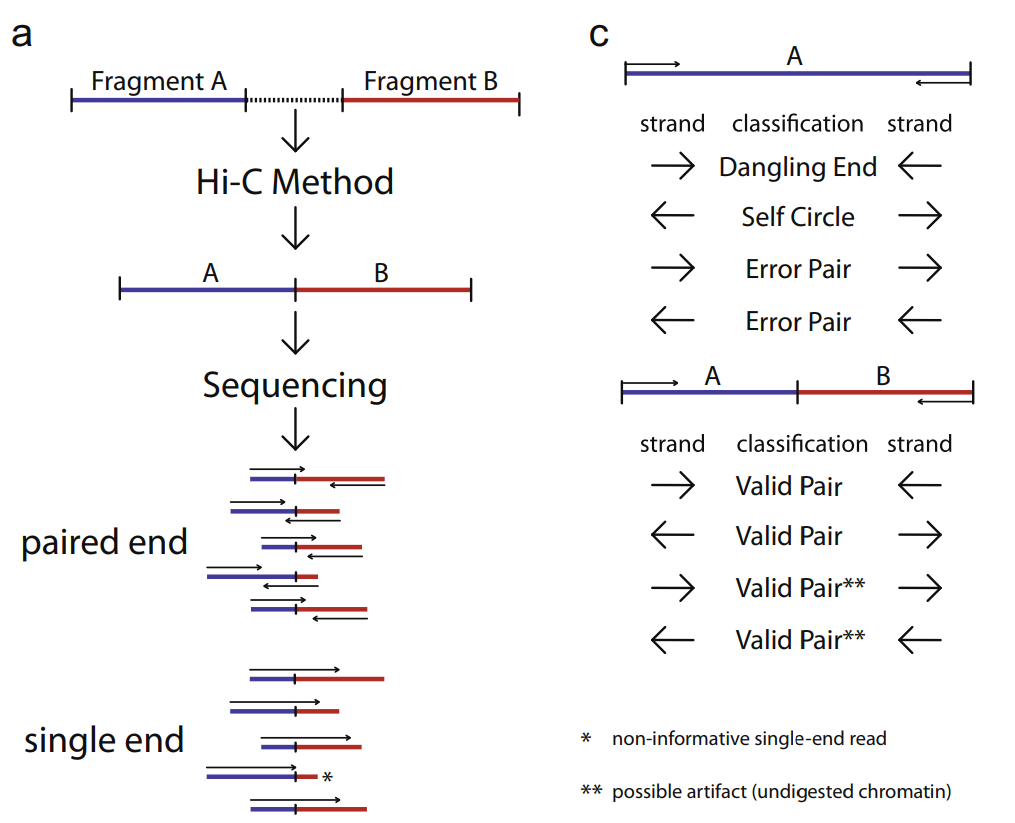
Valid pairs¶
ref: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1046202314003582?via%3Dihub
The figure (Fig.2 from ref) below provides an illustration of all different pairing types.
Multi-mapping issue¶
Our 20copy data has 20 virus insertion sites, bowtie2 just randomly report 1. This could be bad for us.
We might need to correct the bam output.
https://www.biostars.org/p/118301/
https://github.com/nservant/HiC-Pro/issues/403
These trans- pairs will not be included in captureC bw, HiC matrix, or TAD calculation. We can “rescue” these reads by modifying mergeSAM.py. Contact me if you want to do it.
Since these trans- pairs are totally randomly assigned, it should not create any bias, so we only lose some sensitivity for detecting “weak” signals. When we are more care about specificity, we don’t really need to “rescus” these reads, because modifying the code and then test it could cost some time.
generate hic bw file¶
run_lsf.py -f mm10.bam.list -p bwt2pairs_to_bw -g custom --chrom_size /home/yli11/Data/Mouse/mm10/annotation/mm10.chrom.sizes
visualization hicpro result¶
FAQ¶
Out of memory error¶
We requested 160G memory, but it may not be enough. In case that your data is partly processed, you can continue from where it stopped using the following commands:
cd /home/yli11/dirs/blood_regulome/chenggrp/Projects/tcells/HiC/HiC_2_3/hic_hichip_qqi_2020-02-24/Tcell_HiC_2_3/hicpro_results
time HiC-Pro -c hicpro.config.txt -i bowtie_results/bwt2 -o . -s proc_hic
time HiC-Pro -c hicpro.config.txt -i bowtie_results/bwt2 -o . -s quality_checks
time HiC-Pro -c hicpro.config.txt -i hic_results/data/ -o . -s merge_persample
time HiC-Pro -c hicpro.config.txt -i hic_results/data/ -o . -s build_contact_maps
time HiC-Pro -c hicpro.config.txt -i hic_results/matrix/ -o . -s ice_norm
source activate /home/yli11/.conda/envs/multiQC/
export LC_ALL=en_US.utf-8
export LANG=en_US.utf-8
multiqc .
hicpro_split.py¶
Use hicpro_split.py if you have a custom genome
usage: hicpro_split.py [-h] [-j JID] [--split_fastq] [--queue QUEUE]
[--hicpro_config HICPRO_CONFIG]
[--hichipper_config HICHIPPER_CONFIG]
[--MAPS_config MAPS_CONFIG] [-a ANCHOR]
[--cutsite CUTSITE] -r1 R1 -r2 R2 -s SAMPLE_ID
[-t TARGET_BED] [--interactive] [--rerun] [--debug]
[--keep_dup] [-g GENOME] [-i INDEX_FILE]
[--chrom_size CHROM_SIZE] [-e DIGESTED_ENZYME]
[--chr_count CHR_COUNT] [--ref_genome REF_GENOME]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-j JID, --jid JID enter a job ID, which is used to make a new directory.
Every output will be moved into this folder. (default:
hicpro_split_yli11_2020-11-25)
--split_fastq only run hicpro (default: False)
--queue QUEUE
--hicpro_config HICPRO_CONFIG
--hichipper_config HICHIPPER_CONFIG
--MAPS_config MAPS_CONFIG
-a ANCHOR, --anchor ANCHOR
anchor list to search for interactions, if given, MAPS
will be run as well (default: None)
--cutsite CUTSITE Mbol cut site (default: GATC)
-r1 R1 fastq R1 (default: None)
-r2 R2 fastq R2 (default: None)
-s SAMPLE_ID, --sample_id SAMPLE_ID
sample ID (default: None)
-t TARGET_BED, --target_bed TARGET_BED
for captureC (default: None)
--interactive run pipeline interatively (default: False)
--rerun rerun (default: False)
--debug debug (default: False)
--keep_dup use this option to keep dup and keep multi-mapped
reads (default: False)
Genome Info:
-g GENOME, --genome GENOME
genome version: hg19, hg38, mm9, mm10. By default,
specifying a genome version will automatically update
index file, black list, chrom size and
effectiveGenomeSize, unless a user explicitly sets
those options. (default: hg19)
-i INDEX_FILE, --index_file INDEX_FILE
bowtie2 index file (default:
/home/yli11/Data/Human/hg19/index/bowtie2_index/hg19)
--chrom_size CHROM_SIZE
chrome size (default: /home/yli11/Data/Human/hg19/anno
tations/hg19_main.chrom.sizes)
-e DIGESTED_ENZYME, --digested_enzyme DIGESTED_ENZYME
digested_fragments hg19_MboI (default: MboI)
--chr_count CHR_COUNT
chr_count (default: 22)
--ref_genome REF_GENOME
incase input is hg19_20copy, but you still want to use
hg19 in other programs (default: None)
Go to your fastq files folder and do the following:
hpcf_interactive
module load python/2.7.13
bsub -P hicpro -q priority -R rusage[mem=8000] hicpro_split.py -r1 Tcell_HiC_2_3_4_R1.fastq.gz -r2 Tcell_HiC_2_3_4_R2.fastq.gz -s Tcell_HiC_2_3_4 -g hg38
For custom genome, first please generate the correct format for hicpro: hicpro_genome.py
Then use the following parameters:
bsub -P hicpro -q priority -R rusage[mem=8000] hicpro_split.py -r1 Tcell_HiC_2_3_4_R1.fastq.gz -r2 Tcell_HiC_2_3_4_R2.fastq.gz -s Tcell_HiC_2_3_4 -g custom -i PATH/TO/FILE -e PATH/TO/[restriction enzyme bed] --chrom_size PATH/TO/FILE --chr_count N
chr_count is the number of chromosomes in your custom genome, please use an integer here.
Target.bed for capture-C analysis¶
Creating target.bed is little bit complicated, we have automated this part on 4/30/2021. So you don’t need to read this section any more.
You need -t target.bed for starting capture-C analysis. The output is in $jid/hicpro_results/$SAMPLE_ID.bdg. QC can be found in multiQC.html and in the log_file/paris*.err
In multiQC.html, you can check mapping rate, % of uniquely mapped reads and % of valid pairs. In log_file/paris*.err, you will see:
CAP-REP read pairs = 11022
CAP-CAP read pairs = 0
REP-REP read pairs = 4129
Excluded reads = 929
UA reads = 0
Here, CAP is the read mapped to capture (target.bed), reads mapped to +-1000bp were removed, all other reads are REP , so 11022 is the valid capture pairs, also the sum of the bdg values.
A note for writing target.bed.
Target.bed has to be 4 columns: chr, start, end, name. The coordinate has to match the RE bed file. Example:
more target.bed
chr11_paternal 33917808 33917929 v1
chr11_paternal 33918703 33918824 v2
grep 33917808 MboI_resfrag_hg19_ins7.bed
chr11_paternal 33917808 33918820 HIC_chr11_paternal_82356 0 +
The following two baits in from the same RE fragment, so target.bed should be:
chr11_paternal 33917808 33918820 HIC_chr11_paternal_82356
Note that if multiple bait regions are in target.bed, then the output bdg file will likely to have duplicate interaction sites (i.e., OE (other end) sites). You have to groupby the same region and sum up the values to produce a clean bdg file for creating bw file.
Rerun failed exp¶
hicpro_split.py -r1 Jurkat_20copy.R1.fastq.gz -r2 Jurkat_20copy.R2.fastq.gz --sample_id Jurkat_20copy --jid hicpro_batch_yli11_2020-07-06_Jurkat_20copy -g hg19_20copy --rerun
Use --rerun option, match sample id, jid and genome.
captureC¶
Use -t option
The target.bed should have at least 4 columns: chr, start, end, name
hicpro_split.py -r1 ${COL1} -r2 ${COL2} --sample_id ${COL3} -t /research/rgs01/project_space/chenggrp/blood_regulome/chenggrp/Sequencing_runs/rwu_data/newCaptureC/target.bed -g HBG1 -j ${COL3}_hicpro_captureC
if you want to keep duplicated reads and multi-mapped reads, use --keep_dup.
We have pre-defined custom hg19 genomes: e.g., HBG1, hg19_copy
hicpro_split.py -r1 Jurkat_20copy_cassette_captureC_combine_R1.fastq.gz -r2 Jurkat_20copy_cassette_captureC_combine_R2.fastq.gz -s jurkat_20copy -g hg19_20copy -t hg19_20copy_cassette_bait.bed --keep_dup
By 4/30/2021, abs path is not required any more.
Custom genome¶
Use -g custom to specify a custom genome, which needs abs PATH to -i, the index, --chrom_size chromosome size bed file, -e, the digested bed file, and --ref_genome for the prefix of the bowtie2 index. These files can be generated using hicpro_genome.py.
The bowtie index file, -i needs the dir name without the prefix, so it should be bowtie2_index, instead of bowtie2_index/hg19 , and you can specify the prefix using --ref_genome
hicpro_split.py -r1 ../reads/Insulator_7_S22_R1_001.fastq.gz -r2 ../reads/Insulator_7_S22_R2_001.fastq.gz -s ins7 -g custom -i $PWD/../insertion_ref/ins7/hicpro_ref/hicpro_genome_dshresth_2020-11-29/bowtie2_index --chrom_size $PWD/../insertion_ref/ins7/hicpro_ref/hicpro_genome_dshresth_2020-11-29/chrom_size/hg19.chrom.sizes --chr_count 1 -t target.bed -e $PWD/../insertion_ref/ins7/hicpro_ref/hicpro_genome_dshresth_2020-11-29/MboI_resfrag_hg19.bed --ref_genome hg19
Fastq read order¶
This pipeline requires the read names in the same order. If not, use:
$i=test.fastq
fastq-sort -i $i > $i.st.fastq
notes¶
It is hard to compare HiC data with different quality. The main factor is the % of long-range cis- interactions (>20kb). >40% is a high quality data.
HiCExplorer TAD score is based on z-score (Obs/Exp Matrix), sequencing depth should not affect that much. But samples with different noise, technical biases, etc, they will have different TAD scores. You can try tuning the parameters (not suggested):
step mainly affects the speed, also decided by (minD, maxD)
maxDepth will affect how long you want the obs/exp to be calculated
(minD, maxD) together affects the TAD scores (avg zscore)
the larger (maxD-minD), the more window it will average, meaning more smooth, lower TAD score
the lower the value, the more “local” changes
TAD domain length and boundary should not be affected that much since it depends on local minima of TAD score
hicFindTADs --matrix input.h5 --correctForMultipleTesting fdr --minDepth 30000 --maxDepth 200000 --step 30000 --outPrefix test -p 4 --chromosomes chr11 --delta 0.1;bedtools intersect -a *bedgraph -b test.bed -u
TADs: TADs are typically enriched either for H3K36me3 marks (example of the left) or for H3K27me3 marks (example on the right) in a mutually exclusive manner. (Ref: Comparison of computational methods for the identification of topologically associating domains)