Analysis of Sci-L3-seq data¶
usage: sci_l3_seq.py [-h] [-j JID] -f INPUT_LIST -b1 BARCODE_1_LIST -b2
BARCODE_2_LIST -b3 BARCODE_3_LIST [--RT_PRIMER RT_PRIMER]
[--TN5_fwd TN5_FWD] [--TN5_rev TN5_REV]
[--UMI_length UMI_LENGTH] [--bc3_length BC3_LENGTH]
[--sp2_length SP2_LENGTH] [--bc2_length BC2_LENGTH]
[--sp1_length SP1_LENGTH] [--bc1_length BC1_LENGTH]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-j JID, --jid JID enter a job ID, which is used to make a new directory.
Every output will be moved into this folder. (default:
sci_l3_seq_yli11_2020-04-22)
-f INPUT_LIST, --input_list INPUT_LIST
3 column bed file, additional columns are OK, but will
be ignored (default: None)
-b1 BARCODE_1_LIST, --barcode_1_list BARCODE_1_LIST
list of barcode 1 sequences (default: None)
-b2 BARCODE_2_LIST, --barcode_2_list BARCODE_2_LIST
list of barcode 2 sequences (default: None)
-b3 BARCODE_3_LIST, --barcode_3_list BARCODE_3_LIST
list of barcode 3 sequences (default: None)
--RT_PRIMER RT_PRIMER
RT_PRIMER seq (default: GGGATGCAGCTCGCTCCTG)
--TN5_fwd TN5_FWD TN5_fwd seq (default: AGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG)
--TN5_rev TN5_REV TN5_rev seq (default: CTGTCTCTTATACACATCT)
--UMI_length UMI_LENGTH
UMI_length (default: 4)
--bc3_length BC3_LENGTH
barcode 3 length (default: 6)
--sp2_length SP2_LENGTH
spacer 2 length (default: 19)
--bc2_length BC2_LENGTH
barcode 2 length (default: 7)
--sp1_length SP1_LENGTH
spacer 1 seq length (default: 6)
--bc1_length BC1_LENGTH
barcode 1 length (default: 8)
Summary¶
Demultiplexing, read mapping, QC for sci-L3-seq
Code is available at: https://github.com/YichaoOU/Sci-L3-seq
Input¶
fastq.tsv
Copy (or use ln -s) your fastq files to your working directory, prepare fastq.tsv using run_lsf.py --guess_input.
The input file fastq.tsv looks like below:
Banana.R1.fastq.gz Banana.R2.fastq.gz Banana Orange.R1.fastq.gz Orange.R2.fastq.gz Orange
barcode list
You need to have 3 lists of barcodes: barcode_1.list, barcode_2.list, barcode_3.list.
==> barcode_1.list <==
TGATATTG
GATCCCGT
==> barcode_2.list <==
AGGTGGC
TAATAGC
==> barcode_3.list <==
ACGCGA
CGCTTG
Usage¶
hpcf_interactive
export PATH=$PATH:"/home/yli11/HemTools/bin"
cd your_working_dir
## copy (or ln -s) your data here
module load python/2.7.13
run_lsf.py --guess_input
sci_l3_seq.py -f fastq.tsv -b1 barcode_1.list -b2 barcode_2.list -b3 barcode_3.list
Output¶
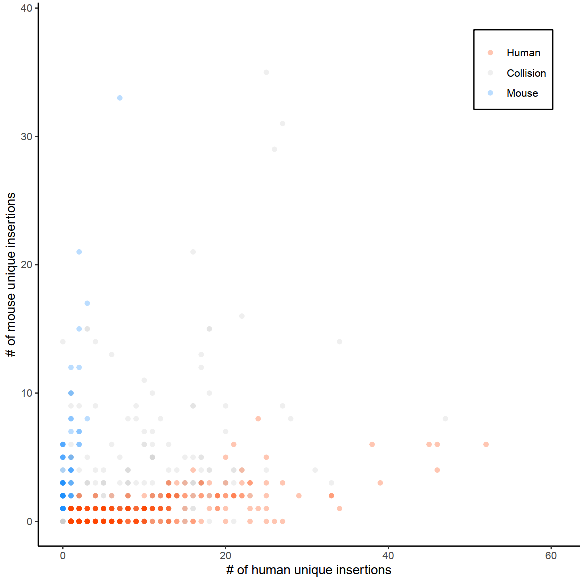
Sample QC (e.g., number of reads contains all the barcodes, collision rate) summary is provided in jid/sample_QC.tsv
An example of collision plot:
BigWiggle files for genome tracks:
[yli11@nodecn204 sci_l3_seq_yli11_2020-04-22]$ find . -name "*.bw"
{{jid}}/KOK675_S2/KOK675_S2_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK675_S2.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK675_S2/KOK675_S2_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK675_S2.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK675_S2/KOK675_S2_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK675_S2.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK675_S2/KOK675_S2_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK675_S2.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK674_S1/KOK674_S1_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK674_S1.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK674_S1/KOK674_S1_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK674_S1.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK674_S1/KOK674_S1_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK674_S1.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK674_S1/KOK674_S1_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK674_S1.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK677_S4/KOK677_S4_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK677_S4.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK677_S4/KOK677_S4_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK677_S4.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK677_S4/KOK677_S4_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK677_S4.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK677_S4/KOK677_S4_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK677_S4.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK676_S3/KOK676_S3_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK676_S3.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK676_S3/KOK676_S3_barcode_demultiplexing/human/KOK676_S3.filter.bw
{{jid}}/KOK676_S3/KOK676_S3_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK676_S3.all.bw
{{jid}}/KOK676_S3/KOK676_S3_barcode_demultiplexing/mouse/KOK676_S3.filter.bw
Notes¶
P5 or P7 sequencing primer are equally possible to be added at the UMI end or gRNA end. So de-multiplexing should look at both R1 and R2 reads.
The reads that we can used to do demultiplexing (R1 or R2) should have this format: UMI (4nt) + SSS_barcode (6nt) + GGGATGCAGCTCGCTCCTG (20nt, RT_primer) + barcode_2 (7nt) + spacer_sequence (6nt, GTCTTG) + barcode_1 (8nt) + Tn5 (19nt, AGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG) + gRNA
By default, barcode 3 allows no mismatch, barcode 2 and barcode 1 each allows 1 mismatch, RT primer allows 3 mismatch.
Fastq read example¶

The read structure helps to follow the pipeline described below.
Pipeline¶
step1:
given RT_primer, assign PE reads to junk (noRT.fastq.gz) and not_junk
swap R2 R1 if R1 doesn’t have RT_primer
match barcode_3, not matched reads will be discarded (noBC3.fastq.gz)
output barcode_3-RT PE reads to R1.ordered.fastq.gz and R2.ordered.fastq.gz
step2:
given barcode_1, barcode_2, barcode_3, parse files from step 4 to matched or junk, renamed read name if matched
step3:
cutadapt trim using Tn5 sequence
step4:
bwa mapping,
step5:
bedtools bamtobed
step 6:
summerize results to table and figure, provided step3_QC_summary.py step4_calculate_collision_rate.py
Reference¶
https://github.com/Yue-Jiang/sciliantifig